Tea extraction is the initial stage which separates the desired components from the basic ingredients. Depending on raw materials and extraction principles, there are numerous extraction methods, including immersion, microwave-assisted, mechanical, subcritical fluid extraction, and so on. In this article, FGC is going to discuss immersion distraction!
Contents
Introduction
Extraction is one of the key processes in manufacturing ready-to-drink tea. It gives tea its characteristic flavor, taste, and aroma and is also crucial in selecting the beneficial compounds for the final products. Let’s follow this article to get a deep insight into the immersion extraction process in making ready-to-drink tea.
Operating principles of extraction process
Extraction is one of the very first steps in making RTD tea. Extraction means selectively dissolving one or several components of raw materials by exposing them to a solvent. Immersion extraction means soaking the ingredients in a solvent to dissolve the desired chemicals. It can be performed with various solvents and is suitable for many raw materials.
Compared to other extraction techniques, immersion extraction has low equipment requirements, which often contains a container and a solvent. Besides, because it does not require highly sophisticated equipment, this procedure is typically more cost-effective. Immersion enables the solvent to fully penetrate the substance, which may result in greater and more effective extraction.
Water is the most popular solvent in the food and beverage industry, including RTD tea production. The solvent helps remove unnecessary substances to obtain the desired ones. The semi-finished products obtained in this process are tea extracts, which can be used to produce tea-based products.
In tea extraction procedures, tea leaves are soaked in pure water to extract active compounds, such as polyphenols, catechins, and caffeine, and separated into tea soups. It is considered a smart method to separate the essence of tea. Dry tea leaves are loaded into extraction tanks, and the solvent will pass through to extract the soluble substances in the tea. The purpose of this process is to keep the EGCG content and the distinctive taste and aroma of the tea leaves.
Before extracting, tea leaves are cleaned to get rid of any contaminants and dried to reduce moisture. In the extracting step, tea leaves are exposed to solvent in the extraction vessel. The soluble components of the tea leaves are extracted and then separated from the spent leaves.
Changes of tea leaves during extraction
Through the extraction process, tea leaves undergo several changes in many aspects, such as physics, chemistry, and biochemistry.
Chemical changes
During the extraction process, chemical reactions may occur between the raw materials’ components. The speed of the chemical reaction might depend on the temperature of the solvent. When extracting tea leaves under high-temperature conditions, reactions between amino acids and polyphenols produce volatile aldehydes, giving the tea its aroma. Several amino acids, such as alanine and phenylalanine, will reduce while aldehyde content increases correspondingly. Additionally, amino acids can react with reducing sugars to create the hue and aroma of tea.
Physical changes
Diffusion is one of the crucial physical changes that make the extraction process faster and more thoroughly. The driving force of diffusion is concentration difference. In addition, the constituents from raw materials may dissolve into the solvent. Moreover, during the extraction process, other phase changes may also occur, like evaporation or precipitation.
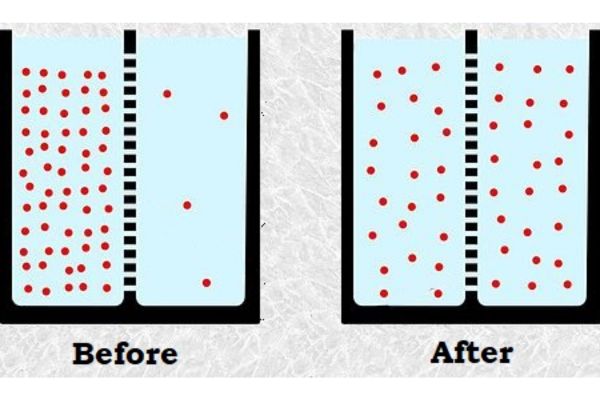
Biological and biochemical changes
Under the effects of temperature, most of the microorganisms in fresh tea leaves are inhibited or destroyed. Except for making cold brew tea, other tea leaf extraction usually happens under high temperatures. High temperatures can inactivate oxidizing and hydrolytic enzymes.
Sensory changes
In addition to the physical and biochemical changes, tea liquor undergoes several alterations in appearance, aroma, texture, or flavor. Sensory-wise, the extracted tea liquor has a darker color and a distinctive smell.
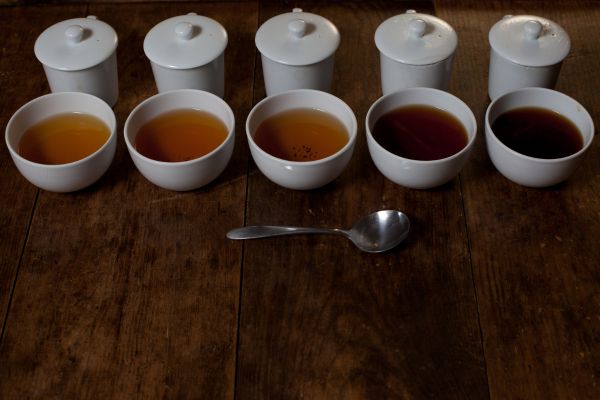

Factors affecting extraction process
The main factors affecting the extraction process include material characteristics, water temperature, the ratio of material to solvent, and the extraction time and frequency.
Material’s characteristics
The smaller the raw material size is, the larger the contact surface between it and the solvent is. Therefore, the extraction might become faster and easier to get the desired components. However, if the materials are too small, the cost of the crushing process might increase. It is also more difficult to filter the liquid from the spent tea leaves. In addition, the material sizes can affect the extraction time and temperature. The bigger it is, the longer the time needed to extract.
Tea leaves’ moisture also affects the extraction process. Water is the medium in which the interactions between soluble substances occur. Therefore, high moisture content can make the extraction process difficult. For that reason, processing tea leaves before extraction is also crucial.

Temperature
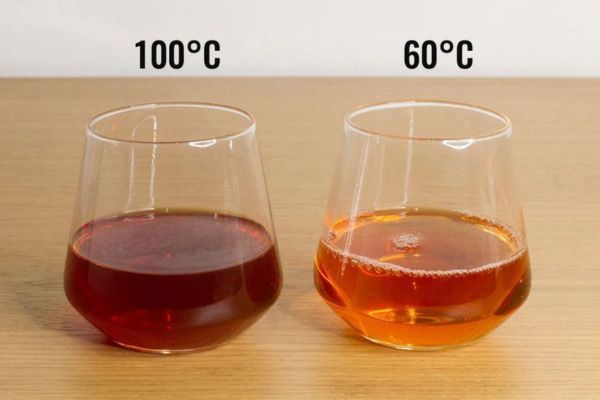
Temperature also plays an important role in extracting tea leaves as it can affect the speed of molecules in the solvent. When the temperature increases, the diffusion and osmosis process will occur more efficiently, and the molecules move faster. In addition, high temperature is used to inactivate enzymes, inhibit microorganisms, and reduce the solvent viscosity, making it easier to penetrate the material layer. It is also a catalytic agent for oxidation reactions of polyphenol compounds.
However, the applied temperature should be calculated carefully. If the temperature is too high, it might destroy the essence of the tea leaves. The temperature rise can also increase energy costs and result in unexpected chemical reactions and aroma loss. For instance, when extracting green tea, the ideal temperature is usually 90°C. This temperature is maintained during extraction for the best efficiency.

The ratio of tea to water
Manufacturers need to determine the appropriate ratio of the materials and solvent, which also means the proportion of tea to water, to avoid waste as well as increase extraction efficiency. If there is too little solvent, the extraction will not be thorough, leading to a waste of time. When the amount of solvent rises, the extraction efficiency will be enhanced. This is because the concentration difference between the constituents that need to be extracted in the material and solvent will be more considerable. Nevertheless, too much solvent can dilute the extract, leading to a concentration process to remove the solvent.
For green tea extraction, the ratio of tea to water commonly used is from 1:40 to 1:60. This rate can also affect the brix degrees of the outcome products as well as the taste of the extracted liquor. With the same amount of solvent, if the quantity of tea leaves increases, the brix will also go up.
The extraction time and frequency
The longer the extraction time, the higher the extractive recovery efficiency. However, at some points, even if the extraction time increases, the efficiency changes insignificantly. On the contrary, it will cause energy waste. At FGC, solvent tanks are equipped with agitators, which help increase the vibration of the tea leaves, thereby increasing the extraction efficiency.
Explore the Aseptic filling process at FGC:
Conclusion
To produce an RTD tea product, tea leaves need to undergo a strictly controlled extraction process. If extracted properly, the outcome will have a bright green color, not too dark or too light, with a delightful aroma, a pleasant bitterness, and a sweet aftertaste. At FGC’s manufacturing plants, every stage in the extraction process is calculated carefully to ensure that the essence of the tea leaves is well extracted and the drinks are given an aromatic flavor and attractive color.
About Future Generation Co.,Ltd
We are FGC, the leading tea and beverage exporter in Vietnam and one of the biggest tea suppliers in the world. Our tea products are diverse in types, grades, and production methods. We provide customers with Loose tea (such as Black tea, Green tea, and Oolong tea), Herbal tea (such as Rose tea, Chamomile tea, and Lotus tea), and Specialty tea (such as Matcha), RTD Tea, and Tea Bags. Our mission is to become Vietnam’s leading healthy beverage company.
We ensure stable tea sources for domestic markets and exports with vast high-grown tea farms and available herb gardens. Our tea gardens and factories also meet international standards such as ISO, HACCP, KOSHER, HALAL, etc. In addition, we constantly innovate our machinery system, strengthen production capacity, and increase productivity. We also provide private label and customized packaging services for small and medium enterprises.
If you are a tea distributor, tea importer, teashop manager, or even tea lover, we are committed to being your prestigious tea source supplier in Vietnam!
Contact
Address: R4 building, Office Quarter 02, Royal City, 72A Nguyen Trai St., Thanh Xuan Dist., Hanoi.
Phone: +84 24 73 000 125/ +84 24 73 063 369
Mail: info@vietnam-tea.com
Website: https://oem-fgc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fgcvietnamtea










